Quantifying Social Media Reactions
This groundbreaking research used discrete choice modeling to quantify the relative value of different social media reactions, winning the Young ESOMAR Society Award 2019 at the ESOMAR Congress.
Task
Led research to understand and quantify the psychological impact of social media reactions using discrete choice modeling and conjoint analysis.
-
Role
Lead Researcher
-
Organization
ESOMAR Congress & SKIM
-
Date
2019
-
Tools
Discrete Choice Modeling, Conjoint Analysis
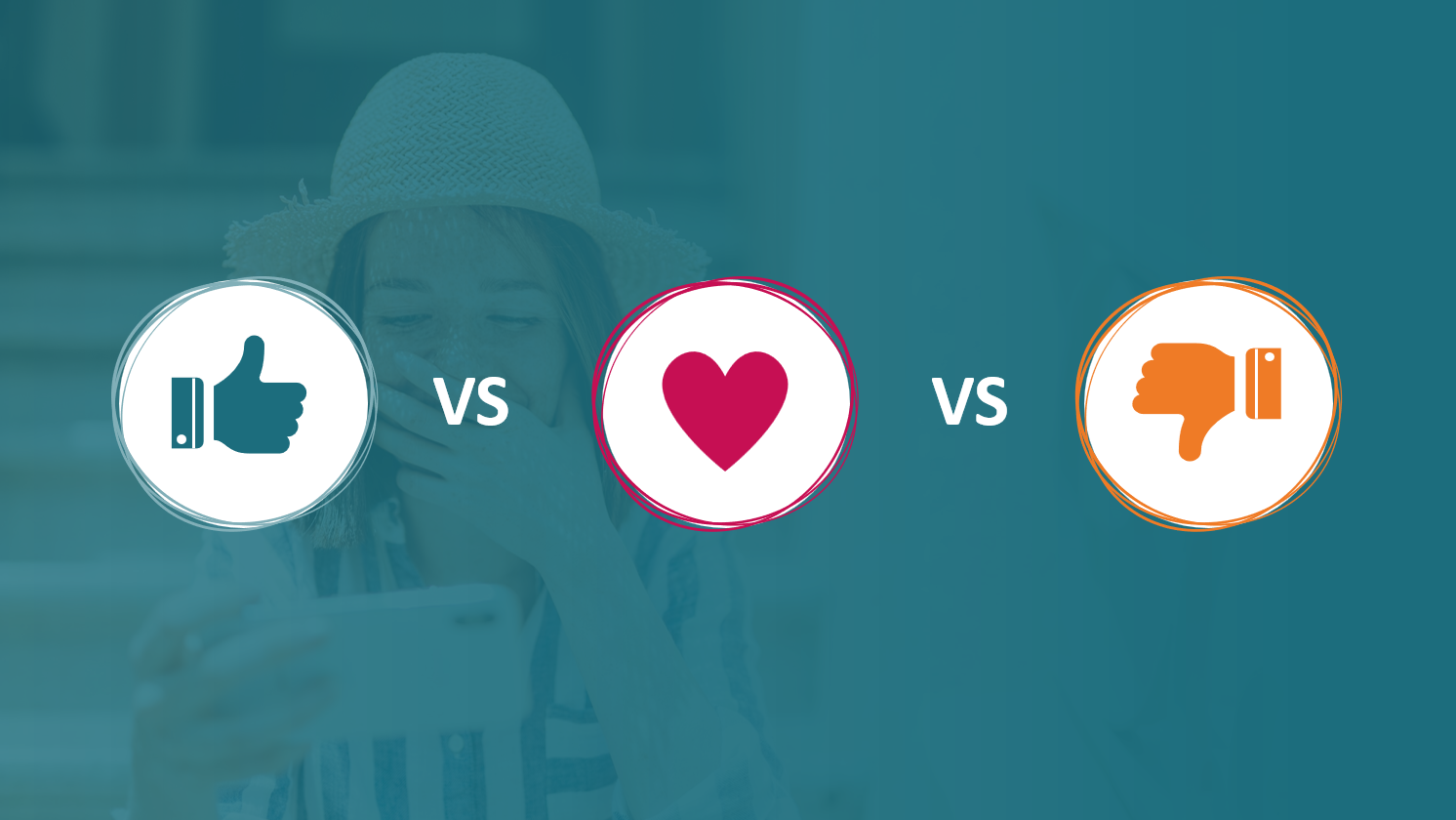
KEY FINDINGS
Research Impact
Our research revealed several groundbreaking insights about how users perceive and process social media reactions:
- One "Love" reaction equals approximately 3.5 "Like" reactions in emotional value, suggesting that more expressive reactions carry significantly more weight
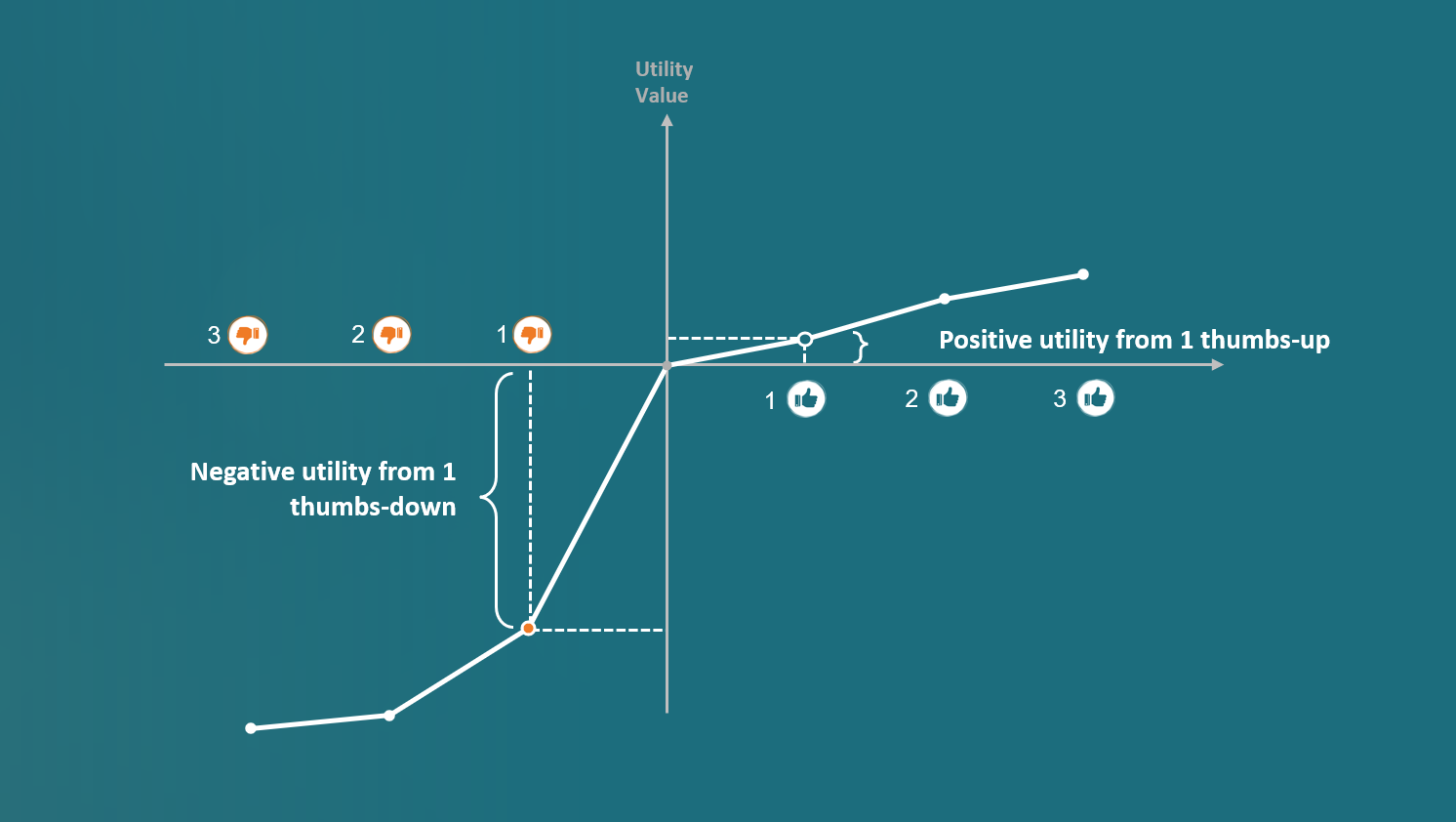
- A single "Thumbs Down" reaction requires 9.7 "Like" reactions to offset its negative impact, demonstrating the disproportionate impact of negative feedback
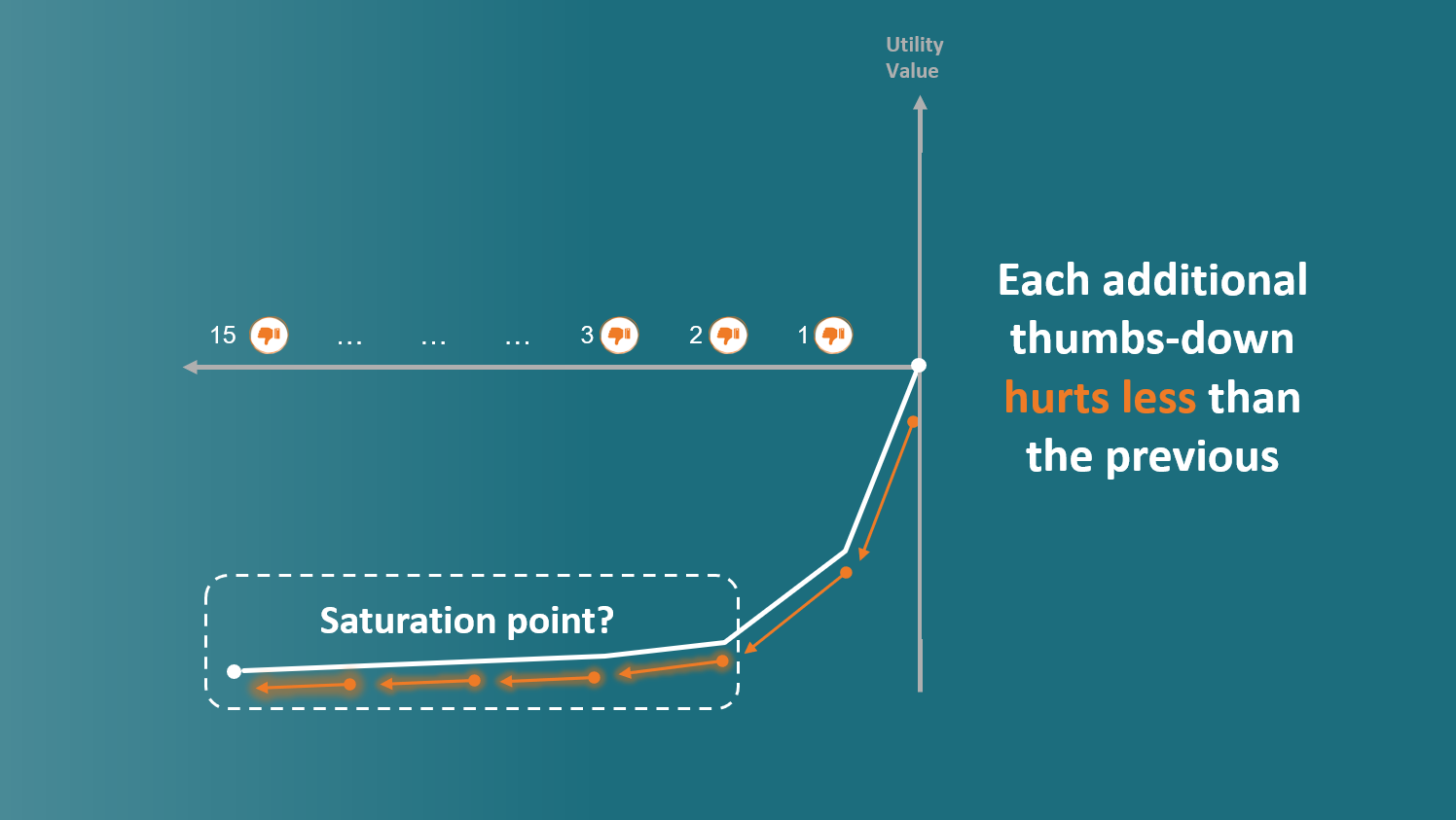
- The impact of negative reactions follows a logarithmic curve, showing diminishing impact over time - similar to psychological habituation
- Context matters: reactions have different emotional impacts based on post content (e.g., personal achievements vs. casual updates)
- Demographic variations: younger users (18-24) showed more resilience to negative reactions compared to older users
- The findings challenge current social media metrics that treat all reactions equally
These insights have significant implications for:
- Social media platforms designing reaction systems
- Brands measuring social media engagement
- Content creators optimizing their strategies
- Mental health professionals understanding online interactions
METHODOLOGY
Research Approach
The study employed a conjoint experiment (discrete choice modeling) with 200 US respondents. Participants were presented with varying combinations of thumbs up, thumbs down, and love reactions, and asked to evaluate which combination would make them feel best if received on their social media post.
Our research revealed two fascinating psychological phenomena:
- Asymmetric Impact: The negative emotional impact of a thumbs down is dramatically stronger than the positive impact of a thumbs up
- Emotional Desensitization: As the number of negative reactions increases, their marginal negative impact decreases
IMPACT
Implications & Recognition
This research challenges the conventional method of measuring social media engagement by simply summing up reactions. Key implications include:
- Need for weighted engagement metrics that account for reaction types
- Importance of considering post context when interpreting negative reactions
- Value of segmenting reactions by demographics and audience type
- Potential for creating more nuanced social media success metrics
Share this post